A bank guarantee and a letter of credit are both financial institution guarantees that a borrower will be able to repay a loan to another party, regardless of the debtor's financial circumstances. While bank guarantees and letters of credit are distinct, both tell a third party that if the borrower is unable to repay its debts, the financial institution will intervene on the borrower's behalf.
These pledges serve to reduce risk factors by providing financial backing for the borrowing party (sometimes at the request of the other). This encourages the transaction to proceed. However, they function in slightly different ways and in various circumstances.
Due to the distance involved, the potential for differing legislation in the nations of the businesses involved, and the difficulties of the parties meeting in person, letters of credit are extremely significant in international trade. While letters of credit are most commonly utilised in international transactions, bank guarantees are frequently used in real estate and infrastructure projects.
Differences between Bank Guarantee and Letter of Credit
Bank Guarantee
A bank guarantee is a contract in which the bank guarantees to the beneficiary, on behalf of the customer, that the bank will be responsible for payment if the customer fails to meet his or her obligations. The bank acts as a guarantee in this agreement, promising to repay the amount within three working days if the applicant fails to pay.
These are employed to mitigate the risk of loss associated with business contracts. The bank receives a commission based on the amount guaranteed for doing so. Furthermore, the bank is not obligated to make payment, and it can refuse to do so if the claim is discovered to be illegal. A bank guarantee can be one of following types:
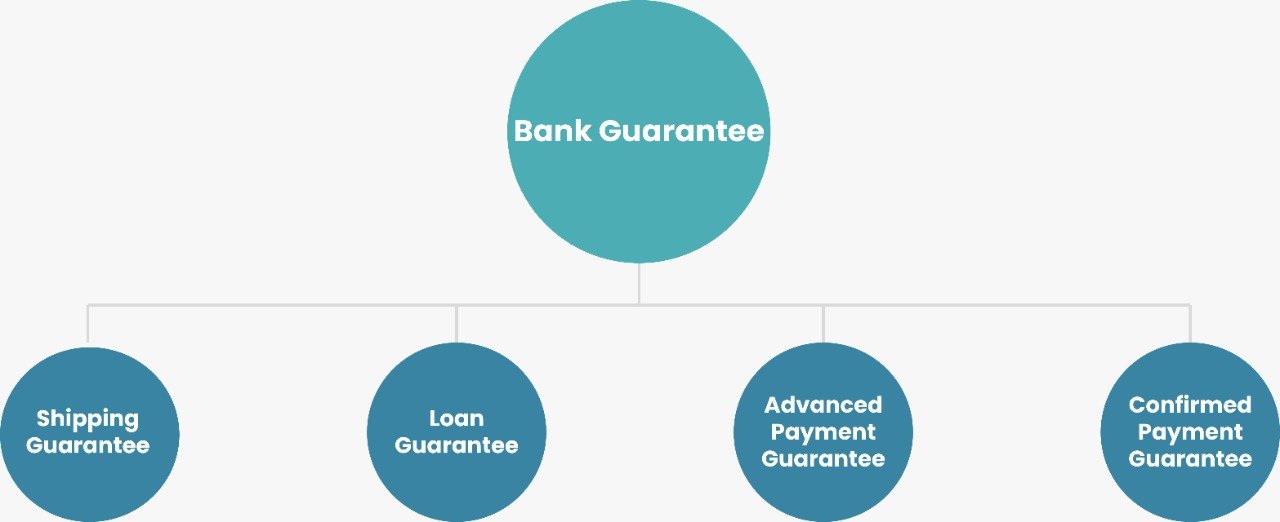
Shipping Guarantees:
A carrier is offered this type of guarantee if a shipment arrives before any documentation are received.
Loan Guarantees:
If a borrower defaults on a loan, the institution that issued the guarantee promises to cover the financial obligation.
Advanced Payment Guarantees:
This guarantee serves to back up the fulfillment of a contract. This guarantee is essentially a sort of collateral used to reimburse an advance payment if the seller fails to deliver the products indicated in the contract.
Confirmed Payment Guarantees:
With this irrevocable obligation, the bank pays a particular sum to a beneficiary on the client's behalf by a specific date.
Letter of Credit
A letter of credit is a formal document that a bank issues to the seller on behalf of the buyer. The agreement indicates that the bank will honour the buyer's draughts for the items given to him if the supplier meets the conditions spelled out in the contract (seller).
The seller has to adhere to all of the buyer's terms and conditions as mentioned in the letter of credit. He must also produce documentary evidence, as well as the required shipment papers, to establish compliance with the terms. The bank will transfer the monies to the seller after the requirements and conditions are met. The letter of credit serves the following purposes:
- If the bank has a solid reputation, the credit risk is removed.
- There is less uncertainty because the merchant is aware of the conditions that must be met in order to obtain payment.
- Provides security to the buyer by allowing them to pay only if the L/requirements C's are met.
Types of Letter of Credit
- A buyer's obligation to the seller is guaranteed by an irrevocable letter of credit.
- When the first bank has doubtful credit, a confirmed letter of credit is issued by a second bank that guarantees the letter. In the event that the company or issuing bank fails to meet their obligations, the confirming bank secures payment.
- An import letter of credit provides a short-term financial advance to importers, allowing them to make payments instantly.
- An export letter of credit informs the buyer's bank that it is obligated to pay the seller if all of the contract's terms are met.
- A revolving letter of credit allows consumers to make limited withdrawals over a set period of time.
The Most Significant Differences between a Letter of Credit and a Bank Guarantee
In terms of the distinction between a letter of credit and a bank guarantee, the following points are noteworthy:
- A letter of credit is a promise from the buyer's bank to the seller's bank that it would accept the seller's invoices and pay them, subject to specific conditions. The term "bank guarantee" refers to a guarantee made by the bank to the beneficiary on behalf of the applicant to execute payment if the applicant defaults on payment.
- The principal liability in a letter of credit is with the bank, which collects payment from the client afterwards. In a bank guarantee, on the other hand, the bank bears liability if the client fails to pay.
- The letter of credit carries a higher risk for the bank but a lower risk for the merchant. The bank guarantee, on the other hand, is riskier for the merchant but less dangerous for the bank.
- A letter of credit transaction involves five or more parties, such as the application, beneficiary, issuing bank, advising bank, negotiating bank, and confirming bank (may or may not be). A bank guarantee, on the other hand, involves only three parties: the application, the recipient, and the lender.
- In a letter of credit, the bank pays the amount due as soon as it becomes due, rather than waiting for the applicant to default and the beneficiary to activate the undertaking. A bank guarantee, on the other hand, becomes effective when the applicant fails to pay the recipient.
- A letter of credit guarantees payment as long as the services are delivered in a specific manner. In contrast, a bank guarantee protects against loss if the parties to the guarantee fail to meet the terms of the guarantee.
- For import and export transactions, a letter of credit is appropriate. A bank guarantee, on the other hand, is appropriate for government contracts.
Bank guarantees and letters of credit both operate to mitigate risk in a business agreement or transaction. When a letter of credit or bank guarantee is operational, parties are more inclined to agree to the transaction because they are less liable. These agreements are especially crucial and beneficial in transactions that might otherwise be problematic, such as real estate and international commerce contracts.
Clients who are interested in one of these documents are rigorously screened by banks. A monetary limit is imposed on the agreement when the bank evaluates that the applicant is creditworthy and poses a reasonable risk. The bank agrees to be obligated up to the limit, but not beyond it. The bank agrees to be obligated up to the limit, but not beyond it. This safeguards the bank by establishing a risk threshold.
Conclusion
A letter of credit is commonly used in foreign trade, but it is also becoming more widely utilized in domestic trade. Whether in a worldwide or local market, you must always pay for your purchases, which is made easier by a letter of credit. Bank guarantees, on the other hand, are used to fulfill various business commitments in which the bank acts as a surety and guarantees the recipient, which is required to meet the business requirements. Thus we hope this blog provided you with incite full information. For more information on other related aspects, feel free to check out our website as well.

