Get FREE CONSULTATION with our team of experts! Click here to start!
Bank Street Road,Burjuman,Dubai,UAE
Mon-Sat 9am-6pm
24 X 7 online support
Bank Street Road,Burjuman,Dubai,UAE
Mon-Sat 9am-6pm
24 X 7 online support
UAE is the largest economy for Sukuk bonds with a cumulative estimated value of Dh 135 billion in Sukuk listings. We offer services in Sukuk systems that come in a variety of shapes and sizes and are offered by a number of Islamic banks and financial institutions across the country.
Types of Sukuk:
Sukuk is an Islamic instrument which offers the same market value that is equivalent to that of a conventional bond. The difference is that Sukuk is organized in a sharia compliant manner and it also represents proportionate undivided possession of the underlying asset or the investment.
Sukuk are the financial products whose terms as well as structures comply with that of sharia, with the purpose of creating returns similar to that of conventional fixed-income instruments such as bonds.
UAE is the largest economy for Sukuk bonds with a total estimated value of Dh 135 billion in Sukuk listings. There are numerous types of Sukuk structures that are offered by numerous Islamic banks and financial institutions in the UAE.
Different from a conventional bond whether it is secured or unsecured. It signifies the debt obligation of the issuer, a Sukuk precisely characterizes an interest in a basic funding arrangement structured as per the sharia. It entitles the holder to a balanced share of the returns that is generated by such arrangement and at a definite future date.
Generally speaking, compliance with sharia states that-
The complete risk profile and financial return for the investor is similar to that of a conventional bond where the holder of the bond is a debtor of the issuer.
The Sukuk issued in international capital markets have been mostly structured as trust certificates, characteristically governed by English law. The several types of Sukuk are explained below-
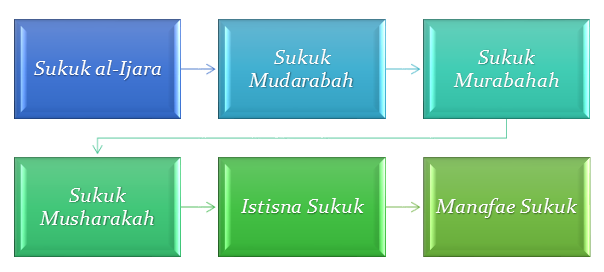
The Sukuk al-Ijara is observed as the most standard Sukuk structure since its allotting began in the year 2008. It is the most popular kind when you anticipate the number of issued sukuks. Shareholders prefer this structure of the Sukuk due to its uncontended agreement with Sharia law. The understanding of how it operates is added factor that draws investors to the Sukuk al-Ijara. If a corporation owns a properties that are free from any debt, the properties can be put up for sale as well as lease.
For people or organizations that does not own any actual tangible assets, it is suitable for them to opt for the Sukuk Mudarabah structure. The owners of Mudarabah sukuks provides capital and they also own equivalent shares of the same value as their invested capital in the Mudarabah pool. Possessors of such bonds can effortlessly sell their Sukuk in the securities market.
In this substitute structure, the corresponding of the Western mark-up principle is utilized. The issuer of this Sukuk obtains the tangible assets and acts as a trustee on behalf of all the holders of Sukuk. The supplies are sold to the holders at a postponed payment. This model of Sukuk is not prevalent owing to its strictness and lack of negotiable instruments.
The Musharakah structure is also relevant for organizations who does not have real tangible assets and consequently cannot benefit from a Sukuk al-Ijara. In this kind of structure, funds are generally mobilized for instituting or developing any business activity.
This type of Sukuk issues certificates to raise funds essential for producing products that are owned by the investors or shareholders.
The Manafae Sukuk structure is established on rights over any underlying assets. The asset has the capacity or rights to perform commercial activities, and also allows for the use of intangible.
Some of the key advantages of issuing a Sukuk market consists of the following-
Some of the disadvantages of the Sukuk in the market consist of the following-
Sukuk are supported by tangible assets rather than any debt. Sukuk possession indicates rights of an asset that has significance. Even though, bond also indicates the same. The real definition of a bond merely specifies a debt obligation. The relationship among the issuer of a bond and the purchaser is very different from that of the relationship between the issuer of Sukuk as well as the buyer of Sukuk. In case of a bond, the customer is performing as the loaner and the bond issuer acts as a loan recipient. In this case, the loan has a fixed rate of interest, consequently being considered as a Riba. In Sukuk, the buyer is buying an asset that has value rather than contributing in an implied loan agreement.
Another important difference between bonds and Sukuk is that the properties involved in Sukuk certificate fulfill with all the laws of Islam. Whereas in the case of bonds, the bond certificate can be backed up by assets that are not compliant with Shariah Law that can be hustled together with other categories of assets without the knowledge of the consumer. The customer of Sukuk is guaranteed that the value of the certificate resembles to assets that are in the public moral and not linked to activities or products that are in contradiction of Islam.
Sukuk, contrasting the bonds are priced as per the real market value of the assets that are supporting the certificate of Sukuk. Bond valuation is based on the credit rating of the issuer. This is required in the case of bonds since when you sell a bond on the secondary market then it is stated that you are actually marketing the debt in the underlying loan connection. The sale of a Sukuk on the secondary market is merely the sale of ownership of the asset.
The main benefit of Sukuk above traditional bonds is that the value surges in relationship to the assets that is supporting the Sukuk certificate. If the asset is raised in value then the value of the possession of that asset is supported by the Sukuk increases eventually. Bonds does not have this feature. It is not imaginable to raise the foremost debt in a bond and intensify the revenue from a bond. It is the direct result of the stable interest.
Sukuk is basically an Islamic version of Conventional Bonds.
Sukuk signify a form of equity as they symbolize certificates discussing ownership to holders of an asset or pool of assets or entitlement to its cash flows.
Yield is a numerical figure that shows the return that you get on a bond. The simplest form of yield is calculated by this formula: Yield = Coupon Amount/Price.