A SWIFT code is required if an international transfer is made. It's normally used in conjunction with an IBAN (International Bank Account Number). When the transfer is complete, the receiving bank sends a ‘SWIFT letter,' which is a confirmation that the funds were received and includes all of the transfer's information.
If you need to send money to a supplier in another country, for example, you'll need to have a SWIFT code. If a customer from another country wants to give you money, they will ask for your SWIFT code.
If you have clients from other countries, this is an essential piece of information to include in your invoice. It speeds up payments by eliminating the need for the customer to request details, and it ensures the security of your transfer.
What is a SWIFT Code?
SWIFT stands for Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication, and it's a code made up of letters and numbers that gives a bank's branch a specific identity. Business Identifier Code, or BIC, is another name for SWIFT codes. It is widely accepted around the world for transferring funds to any bank account.
A swift code is made up of 8 or 11 characters with a break in the centre.
- The first four characters are letters that represent the bank code.
- The swift code's next two characters are the country code, which is written in letters.
- The location code is represented by the next two characters. This can include both letters and numbers.
- The branch code, which can be a mixture of letters and numbers, is represented by the last three characters.
Why is SWIFT important?
SWIFT codes and the SWIFT network are extremely important. Global transactions have become more reliable and efficient as a result of these developments. Since banks can now quickly communicate orders to one another, it has become more secure and less expensive. Since SWIFT uses globally standardised communications, it is a straightforward way for organisations to communicate with one another and easily transfer the particulars of each transaction, which means less costly remittances for senders. SWIFT has a number of well-known advantages:
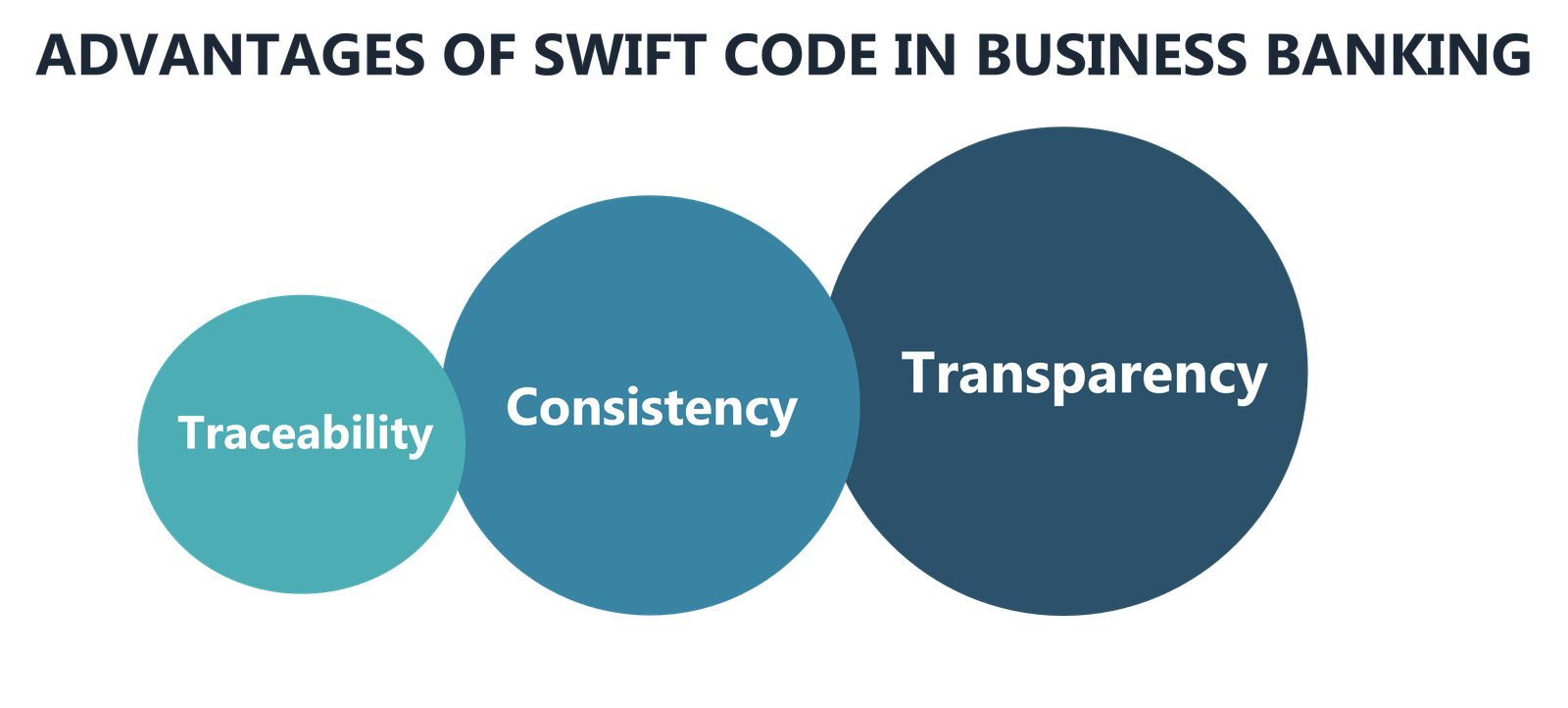
Transparency
SWIFT transfers explicitly show the sums involved in the trade, the path it follows between banks, all costs, and the payment's existence (along with many other details). This information helps those involved in the deal to keep track of it and consider the costs and time frame involved.
Traceability
SWIFT offers straightforward and recognised evidence of payment by detailing the path of the exchange between banks and the amount of money involved.
Consistency
Payment details are simple to understand regardless of nation or language differences due to the accuracy of how communications are organised.
How to find a SWIFT Code for a Bank?
The SWIFT code can be found on bank statements, chequebooks, and online banking portals with ease. If not, a BIC/ SWIFT code generator can be used. Choose the bank and the venue, and then generate the SWIFT code.
When transferring money from one bank account to another, a SWIFT code is needed. Banks can levy a small fee for each transaction.
What is a Correspondent Bank?
A correspondent bank is a financial institution that provides services to another financial institution, typically in a different country. It serves as a middleman or agent for another bank, facilitating wire transfers, performing business transactions, receiving deposits, and collecting documents. Domestic banks would most likely use correspondent banks to serve transactions that originate or are completed in other countries. Correspondent banks are used by domestic banks to gain access to international financial markets and support international clients without having to open branches abroad.
What is an MT103?
An MT103 is a SWIFT payment message used by domestic and cross-border wire transfers. For all payments made by Money Mover, we use SWIFT. MT103s are widely accepted as payment proofs, and they provide all payment information, including the date, number, currency, sender, and receiver. Since they display the payment's route between the banks, MT103s are also useful for tracking payments that have gone missing or are late. Every payment would have an MT103 from all SWIFT-enabled banks and financial institutions, but they are unlikely to offer it to you.
Different ways of Tracking Payment through Swift Messages
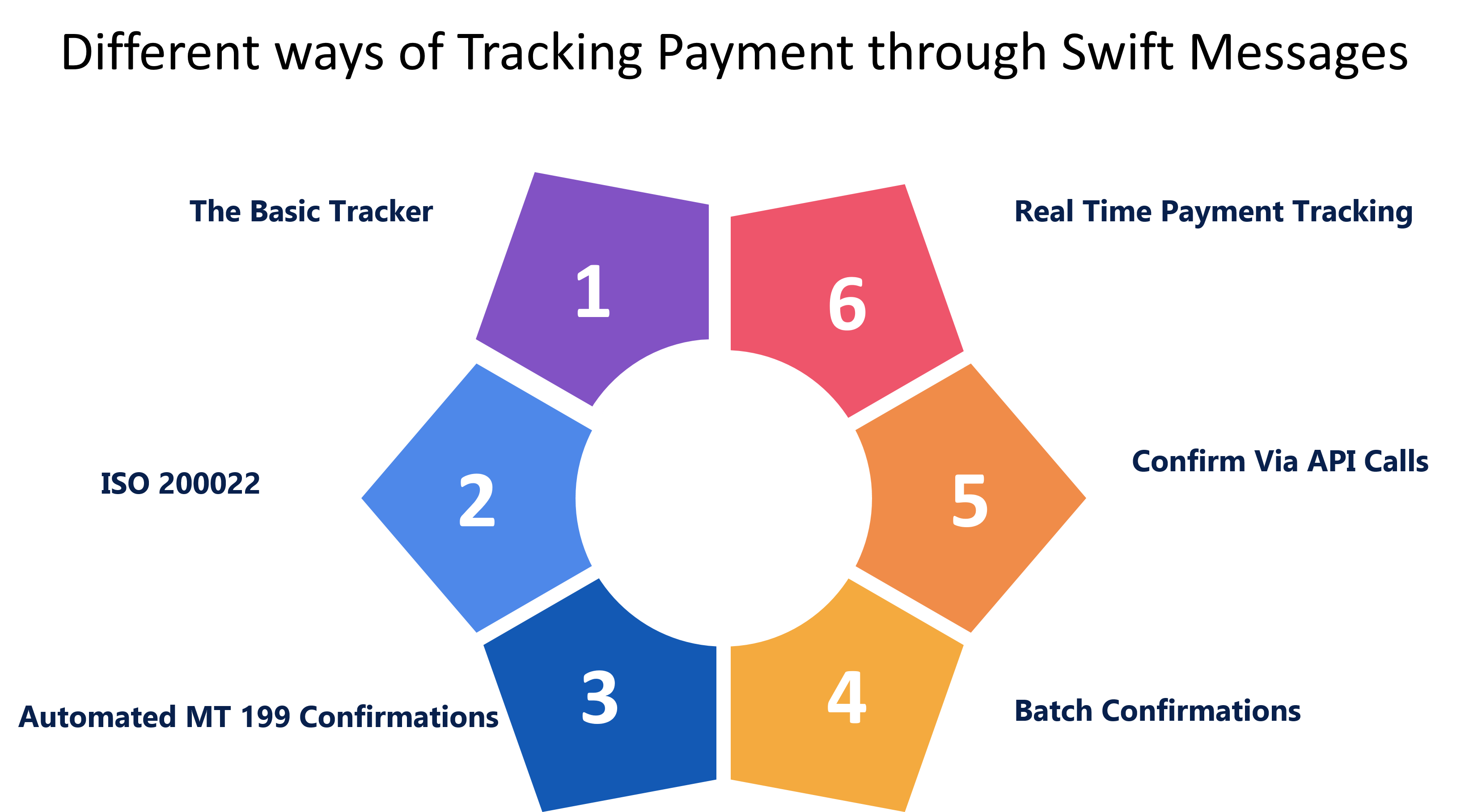

The Basic Tracker
Our free Basic Tracker helps you to manually validate transfers to help non-GPI banks with low cross-border payment volumes.
You can meet payment validation criteria, use basic search and monitoring functionality, verify your compliance with the mandate, and provide a simple upgrading path to the full version of the GPI Tracker if you wish through the Basic Tracker.
Automated MT 199 Confirmations
You will validate your payments by sending an interbank transfer message (MT 199) from your current SWIFT interface to a dedicated GPI Tracker BIC.
The Tracker is updated as a result of this post, and the ordering bank receives payment confirmation.
Batch Confirmations
Universal Confirmations will now be implemented as a single end-of-day export file from your payment framework using our new CSV format (Comma Separated Values).
To use the CSV alternative to validate payments, make sure your payment mechanism (proprietary or from your supplier) can generate the SWIFT CSV format.
The CSV files are consumed by Alliance Access or Admission, which converts each entry into a payment status report to the Tracker.
Confirm via API calls
Using API calls to validate payments is a quick and easy way to keep the GPI Tracker up to date. The SWIFT SDK or the SWIFT Micro gateway can be used by any SWIFT customer to refresh the Tracker with the transaction's special tracking code.
ISO 20022
To give confirmations to the Tracker, an ISO 20022-compliant messaging protocol will be accessible, easing the burden on banks and making the transition from MT easier.
Real-Time Payment Tracking
SWIFT's Board and Executive approved bold proposals to make the SWIFT network richer, smarter, and quicker in March 2020. SWIFT will allow ISO 20022 messages for cross-border payments and cash reporting businesses beginning in the second half of 2022, based on community input. This pushes back the initial deadline by a year.
SWIFT has revealed that its GPI Tracker will now provide all payment directions sent through the network. GPI banks will be able to watch all of their SWIFT payment orders at all times, giving them complete control over their entire payment activity.
Conclusion
SWIFT stands for Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication, and it's a code that is made up of letters and numbers which provides a bank's branch a specific identity. Business Identifier Code, or BIC, is another name for SWIFT codes. It is extensively accepted around the world for transferring funds to any bank account in UAE. Connect with Dhanguard to learn more about Business Banking in UAE.
DhanGuard: All-in-One Solution for Business Setup in Dubai, UAE
DhanGuard is your ultimate one-stop solution for all your business needs. Whether you’re planning to set up a new company or expand your existing business in the UAE, we’ve got you covered with our comprehensive range of services. From Business Setup in UAE and Company Formation in Dubai to managing your financial and legal compliance, we provide everything you need under one roof.
Our services include:
- Company Formation in UAE and Dubai
- Opening a Business Bank Account in UAE and Dubai with a 99% success rate
- VAT & Corporate Tax Compliance
- Accounting, Bookkeeping, and Auditing Services
- Trade License Renewal
- Golden Visa Assistance
Let DhanGuard make your journey of Business Setup in Dubai seamless and hassle-free!















